
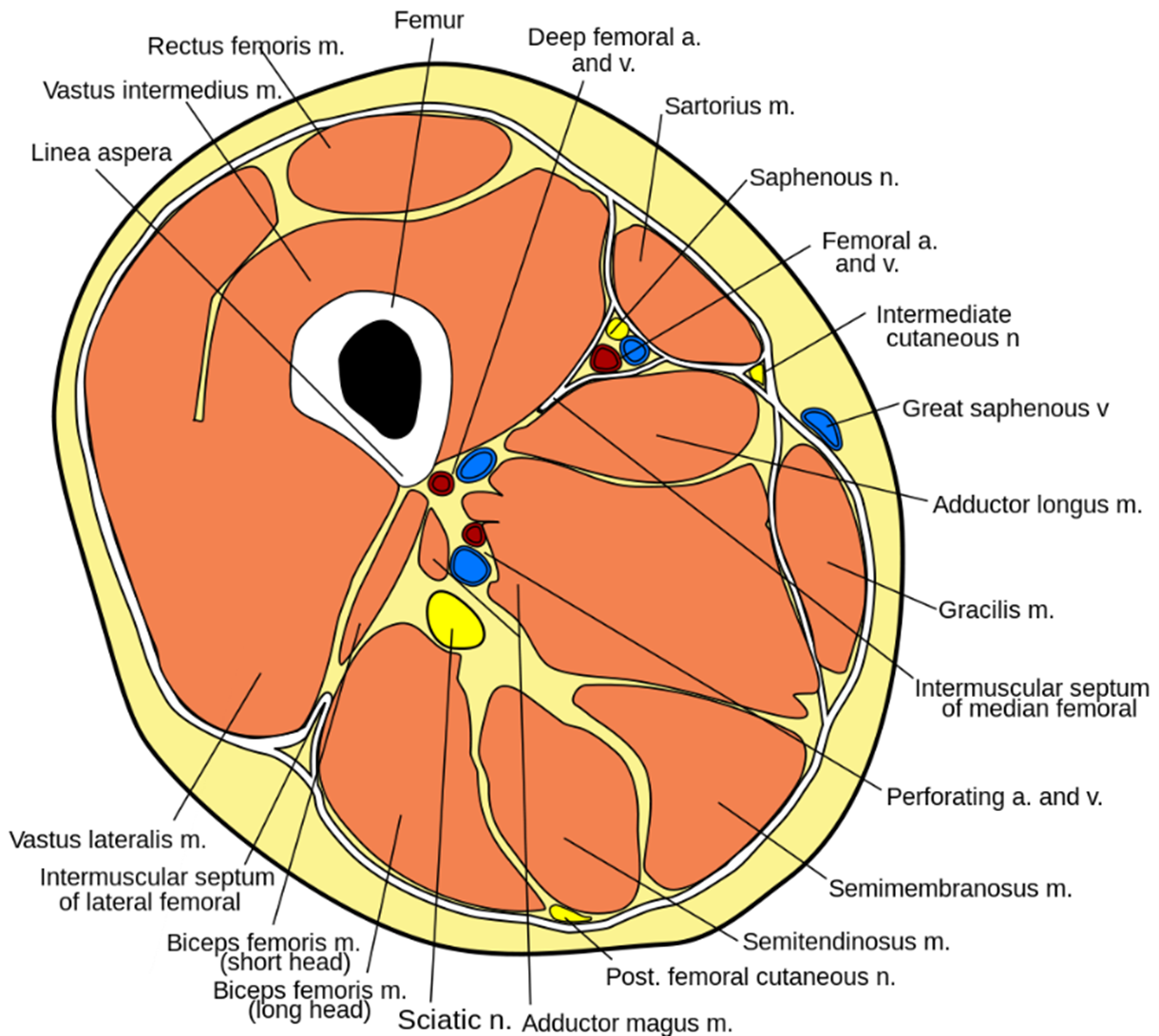
The quadriceps femoris consists of four individual muscles - the three vastus muscles and the rectus femoris. Fig 1 - The muscles of the anterior thigh.
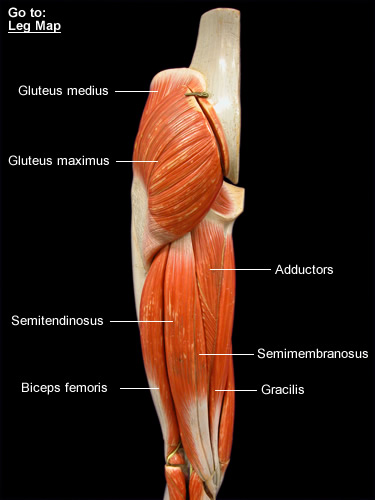
They are collectively innervated by the femoral nerve (L2-L4), and recieve arterial supply from the femoral artery. The muscles of the anterior compartment of the thigh are a group of muscles that (mostly) act to extend the lower limb at the knee joint. As group, these muscles act to extend at the hip, and flex at the knee. They consist of the biceps femoris, semitendinosus and semimembranosus, which form prominent tendons medially and laterally at the back of the knee. The anterior compartment of the thighs comprise. The anterior compartment contains the four muscles of the quadriceps femoris group, as well as four other muscles, but some consider the tensor muscle of the fascia lata with the gluteal region. Actions: Extension of the knee joint and flexion of the hip joint (it is the only muscle of the quadriceps group to cross both the hip and knee joints). The muscles in the posterior compartment of the thigh are collectively known as the hamstrings. The thigh has three compartments of muscles that surround the femuranterior, medial, and posterior.It attaches to the patella via the quadriceps femoris tendon. Attachments: Originates from the anterior inferior iliac spine and the ilium of the pelvis.Proximal attachment: Originates from the intertrochanteric line and medial lip of the linea aspera of the femur.Proximal attachment: Originates from the anterior and lateral surfaces of the femoral shaft.It has a secondary function of stabilising the patella. Proximal attachment: Originates from the greater trochanter and the lateral lip of linea aspera of the femur.Each muscle in the three compartments has a proximal. The patella, in turn, is attached to the tibial tuberosity by the patella ligament. And, more importantly, each compartment contains its own muscles, as well as blood vessels and nerves. The four muscles collectively insert onto the patella via the quadriceps tendon. It forms the main bulk of the anterior thigh, and is one of the most powerful muscles in the body.
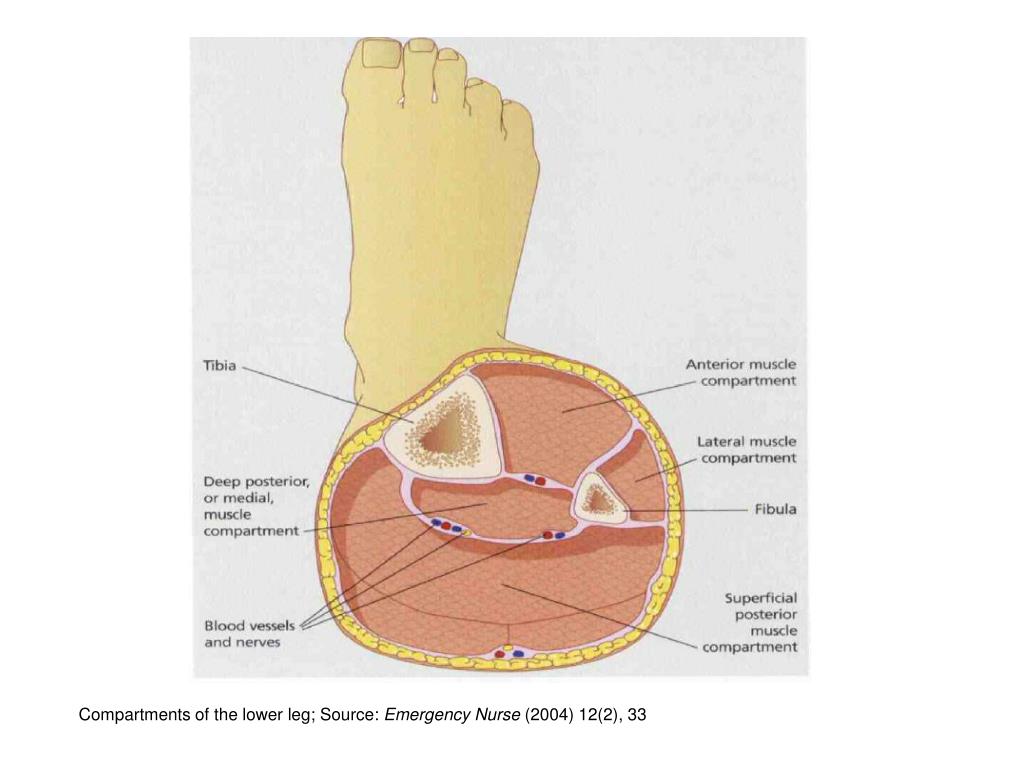
Action: Extension of the great toe and dorsiflexion of the foot.The quadriceps femoris consists of four individual muscles – the three vastus muscles and the rectus femoris.The tendon crosses anterior to the ankle joint and attaches to the base of the distal phalanx of the great toe. Attachments: Originates from the medial surface of the fibular shaft.Its tendon emerges from between the two muscles to insert onto the big toe. The extensor hallucis longus is positioned deep to tibialis anterior and extensor digitorum longus. Actions: Extension of the lateral four toes, and dorsiflexion of the foot.The tendon splits into four and each tendon inserts onto a toe.The fibres converge into a tendon, which travels onto the dorsal surface of the foot.Originates from the lateral condyle of the tibia and the medial surface of the fibula.Its four tendons can be palpated on the dorsal surface of the foot. If it happens suddenly, it can be serious and. The extensor digitorum longus lies laterally and deep to the tibialis anterior. Compartment syndrome is an increase in pressure inside a muscle, which restricts blood flow and causes pain.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
